• All cells in an organism contain all the DNA: – all genetic info
• Must regulate or control which genes are turned on in which cells
• Genes turned on determine cells’ function – E.g.) liver cells express genes for liver enzymes but not genes for stomach enzymes
Proteins act in trans DNA sites act only in cis
• Trans acting elements (not DNA) can diffuse through cytoplasm and act at target DNA sites on any DNA molecule in cell (usually proteins)
• Cis acting elements (DNA sequences) can only influence expression of adjacent genes on same DNA molecule
Eukaryotic Promoters---trans-acting proteins control transcription from class II (RNA pol II) promoters
t: 302px;"/>
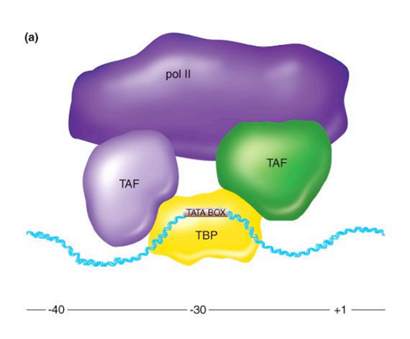
• Basal factors bind to the core promoter – TBP – TATA box binding protein – TAF – TBP associated factors
• RNA polymerase II binds to basal factors
Eukaryotic Promoters
• Promoter proximal elements are required for high levels of transcription. • They are further upstream from the start site, usually at positions between -50 and -500.
• These elements generally function in either orientation.
• Examples include:
– The CAAT box consensus sequence CCAAT
– The GC box consensus sequence GGGCGG
– Octamer consensus sequence AGCTAAAT




